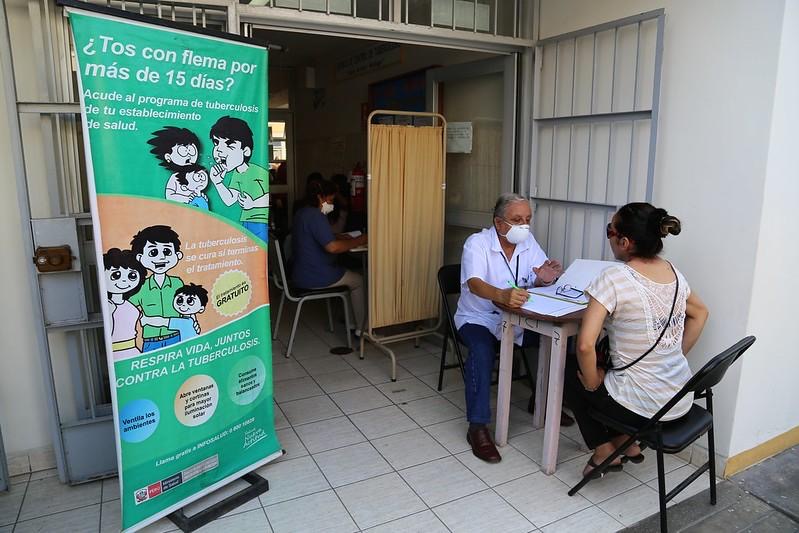
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has published its Global Tuberculosis Report 2024, revealing a concerning increase in TB cases worldwide.
The report in a statement on Tuesday, said approximately 8.2 million people were newly diagnosed with TB in 2023, the highest number since WHO began global TB monitoring in 1995.
According to the report, 10.8 million people fell ill with TB in 2023, with TB remaining the leading infectious disease killer, surpassing COVID-19.
It said the breakdown of cases showed 55 per cent were men, 33 per cent women, and 12 per cent children and young adolescents.
“India, Indonesia, China, the Philippines, and Pakistan account for 56 per cent of the global TB burden.”
WHO Director-General, Dr Tedros Ghebreyesus, expressed outrage that TB continues to kill and sicken millions in spite of available prevention tools.
The challenges, he said include significant underfunding, with global funding decreasing to 5.7 billion dollars (26 per cent of target), and multidrug-resistant TB remaining a public health crisis. Low- and middle-income countries face funding shortages.
WHO urges countries to expand tool usage and end TB, calling for sustained financial investment in TB prevention, diagnosis, and treatment efforts.